1
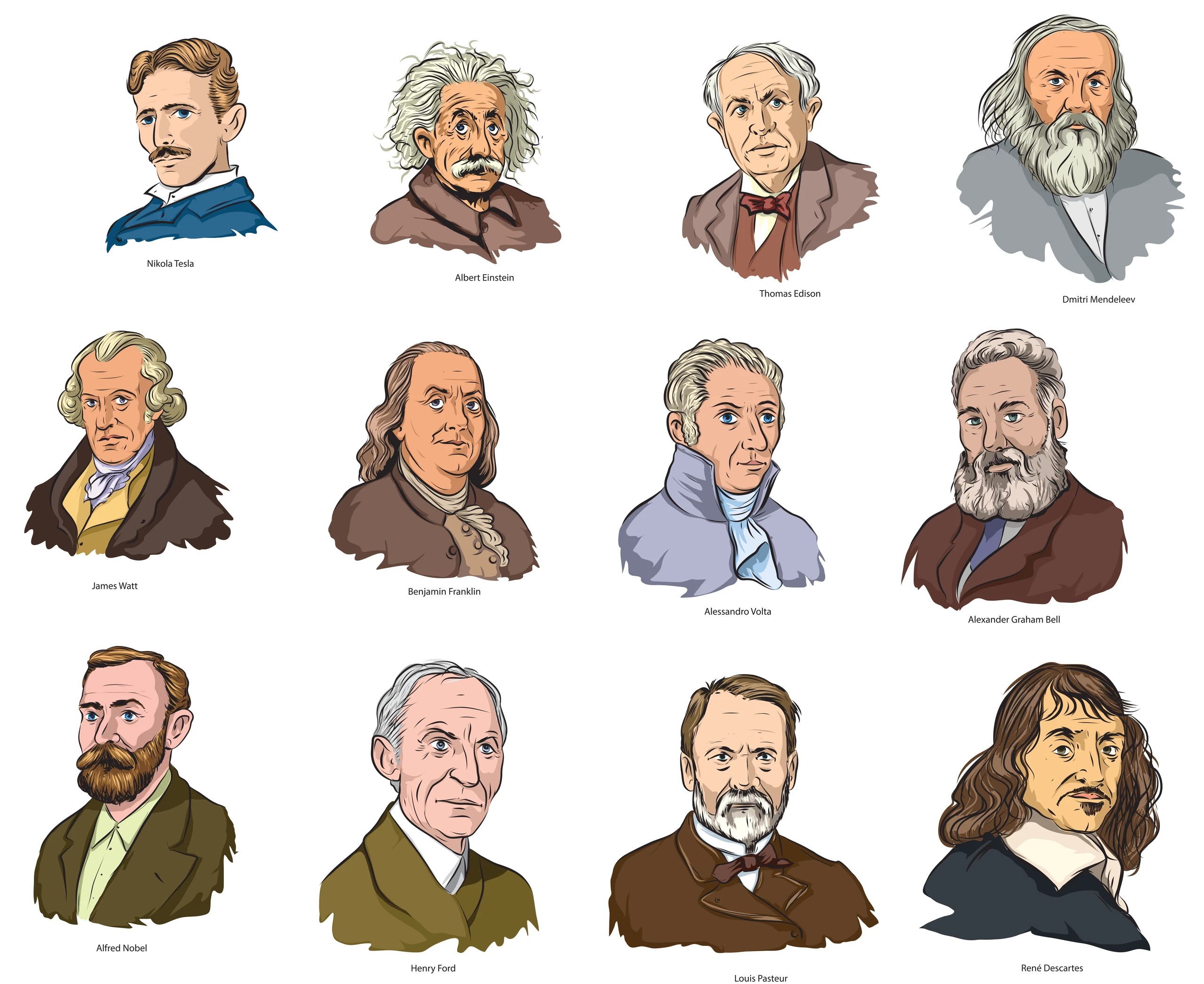
Nikola Tesla
/ˈnɪkələ ˈtɛs.lə/
2
Albert Einstein
/ˈælbərt ˈaɪnstaɪn/
3
Thomas Edison
/ˈtɒməs ˈɛdzən/
4
Dmitri Mendeleev
/dɪˈmɪtri mɛndəˈleɪɛv/
5
James Watt
/dʒeɪmz wɒt/
6
Benjamin Franklin
/ˈbɛndʒəmɪn ˈfræŋklɪn/
7
Alessandro Volta
/ˌælɪˈsændroʊ ˈvoʊltə/
8
Alexander Graham Bell
/ˌælɪɡˈzændər ˈɡreɪəm ˈbɛl/
9
Alfred Nobel
/ˈælfrɛd ˈnoʊbəl/
10
Henry Ford
/ˈhɛnri ˈfɔrd/
11
Louis Pasteur
/luːˈiː pæˈstɜːr/
12
Rene Descartes
/ˈreɪni dɛsˈkɑrt/